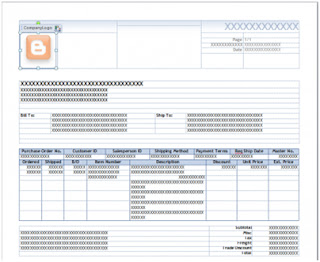
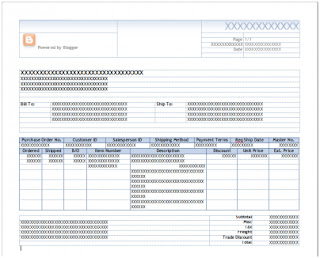
Getting used to the new Word Templates functionality can be a bit challenging at times. One of those challenges came in the form or a simple question: "How to resize the logo on the template?". One thing to keep in mind is that most objects on a Microsoft Dynamics GP Word Template document live inside of content controls. With that said, here are the steps to achieve this, taking the SOP Blank Invoice Form Template* as an example:
1. Under Report Template Maintenance, select the SOP Blank Invoice Form template from the More Reports list.
5. Select the logo, right-click, and chose Remove Content Control.
7. Save the modified template to a different directory where it can be imported from later on, for example, My Documents. Close Microsoft Word.
9. Click the Assign button, then mark the company you want to assign the template to. Then, click on Set as Default to make the new template the default template for the company. Click Save to continue. Click Save to continue.
11. To test, select a SOP invoice and print.
Until next post!